World Backup Day: Protect your data before you lose it
Every year on March 31st, the world observes World Backup Day. The idea was first proposed by Reddit user Adam Jefferson in 2011.
Portmapper (portmap, rpcbind) is an Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call service. It dynamically converts Remote Procedure Call service numbers (such as NIS or NFS) into TCP/UDP port numbers.
The service sends RPC broadcast messages on port 111. This specific feature of portmapper could be used to perform a DDoS attack. The UDP protocol allows IP spoofing. Thus, attackers can send small requests to portmapper using the victim's IP address. As a result the server will send all the replies to the victim's address in a much larger volume when receiving such requests. Such amount of traffic from the service heavily loads the infrastructure resources - servers and network equipment, which in turn may lead to inability or delays in processing requests from normal users, which is the purpose of a DDoS attack.
How to check portmapper activity
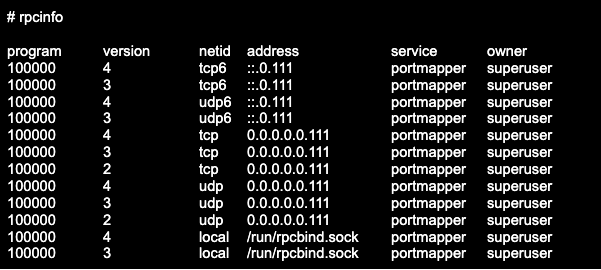
To check whether you have portmapper running on a VPS or a dedicated server, use the utility rpcinfo, which runs an RPC query and displays the registered RPC services. You can check both local and remote hosts.
To check the local host, run the rpcinfo command:
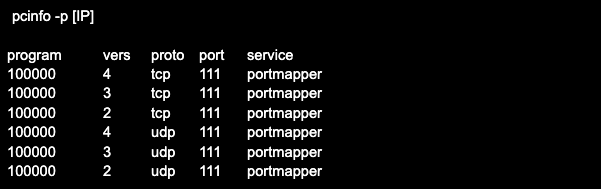
To check a remote host, specify its address, for example after the -p key. Applying the -s key will show the output in shortened form. Example output of rpcinfo command with -p and -s keys:
The options of the rpcinfo utility can be found in the man help, which can be called with the command man rpcinfo (also man rpcbind).
Additionally, a local host check can be performed with the ss utility (netstat). The use and description of the keys for this utility can also be found in the man help. Here is an example (the command header is added separately for clarity):
How to disable portmapper
To disable and remove portmapper (rpcbind) from boot in distributions that use systemd, such as Debian, RHEL, Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, Gentoo, etc., run the command systemctl stop rpcbind.service:
Next, stop the socket with the systemctl command stop rpcbind.socket.
Use the commands systemctl disable rpcbind.service and systemctl disable rpcbind.socket to remove it from the autorun.
If you are using script-based boot scripts in /etc/init.d, you can stop the service with the /etc/init.d/rpcbind stop command.
You can remove it from the autostart in Debian-based distributions by using the update-rc.d -f rpcbind remove command.
In RedHat distributions, you can remove it using the command chkconfig rpcbind off.
After you disable the portmapper service and run the rpcinfo command, you will see an error message:
How to restrict the connection to portmapper
If you still need the portmapper service, you can restrict access to it by, for example, allowing only certain IP addresses to connect. This can be done by using a network filter by restricting access to port 111.
Examples of commands to restrict UDP for IPv4: